Beta-Glucans
The Powerhouse of the Medicinal Mushroom Family
For thousands of years, medicinal mushrooms, also known as functional mushrooms, have played a vital role in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM). Varieties like Reishi, Shiitake, Maitake, Lion’s Mane, Turkey Tail, Chaga, and Cordyceps are revered worldwide for their powerful and extensive health benefits. In the last several decades, scientists have conducted thousands of studies demonstrating their medicinal properties are due in large part to their high concentration of the active compounds known as beta-glucans.
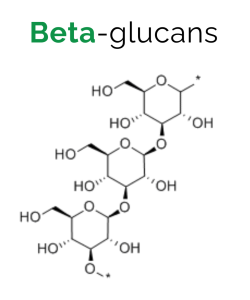

Beta-glucans are complex molecules that come from a family of long-chain carbohydrates known as polysaccharides. The two most common types of polysaccharides found in mushrooms are alpha-glucans and beta-glucans. To understand and distinguish the difference between functional mushrooms’ health benefits, and the medicinal power of mushroom supplement products in general, it is important to understand the difference between the two. Let’s begin by discussing beta-glucans.
Let’s begin with beta-glucans.
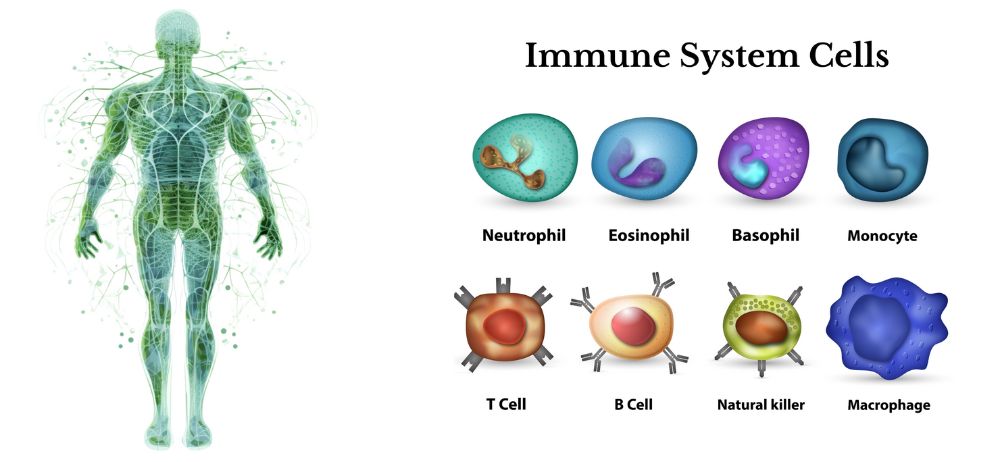
Beta-glucans are like superheroes of the mushroom world, helping our bodies stay well. Their medicinal properties are attributed to two primary factors – their branch-like structure and how much is present in the mushroom. Beta-glucans are exceptional at improving the immune system’s ability to communicate. They stimulate our bone marrow to produce natural killer cells, T-cells, and macrophages, as well as serve as effective biological response modifiers (BRMs). BRM’s possess the ability to turn up or down our immune system responses based on what is necessary. This means they can boost the immune system without triggering harmful overreactions, a critical characteristic for those grappling with autoimmune issues.
In addition to beta-glucans, Chinese medicinal mushrooms contain both soluble and insoluble fiber (prebiotics) that feed healthy gut bacteria (probiotics) who then make for us essential nutrients like short-chain fatty acids (postbiotics). With each mushroom variety possessing its own unique set of beta-glucan benefits, these functional mushrooms are further enhanced by the presence of phytonutrients like triterpenes, ergosterol, ergothioneine, polyphenols, and digestive enzymes.
There are presently more than 20,000 scientific research studies world wide investigating the diverse impact of beta-glucans on health. If you would like to dive deeper visit www.betaglucan.org, home of the Beta-glucan Research Index. This extensive database houses an A-Z compilation of today’s most up-to-date beta-glucan research that is searchable by health condition, research topic, or contribution. They are a non-commercial organization that does not make or support any products.
Alpha-glucans:
Another common type of polysaccharide found in mushrooms is called alpha-glucans, which has almost no medicinal properties (those found in Lions Mane and fermenting them as with AHCC are the exception). If a supplement company claims its product is medicinal and only lists “high amounts of polysaccharides” on the label without specifying the beta-glucan content the product is more than likely misleading. This is because alpha-glucans are also found in starch and most supplement companies are using mushrooms grown on grain. As such, these mushrooms draw their nutrients from the grain’s starch that isn’t filtered out during processing. This means on paper a product may test “high in polysaccharides”, but most of those polysaccharides come from alpha glucans in the form of starches, giving a false indication of their product’s medicinal benefits.
Choose a Mushroom And Learn More!
For thousands of years, medicinal mushrooms, also known as functional mushrooms, have played a vital role in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM). Varieties like Reishi, Shiitake, Maitake, Lion’s Mane, Turkey Tail, Chaga, and Cordyceps are revered worldwide for their powerful and extensive health benefits. In the last several decades, scientists have conducted thousands of studies demonstrating their medicinal properties are due in large part to their high concentration of the active compounds known as beta-glucans.







